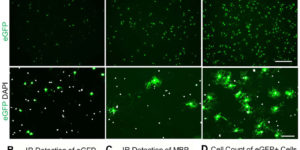
A selective thyroid hormone β receptor agonist enhances human and rodent oligodendrocyte differentiation.
Nerve conduction within the mammalian central nervous system is made efficient by oligodendrocyte-derived myelin. Historically, thyroid hormones have a well described role in regulating oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination during development; however, it remains unclear which thyroid hormone receptors are required to drive these effects. This is a question with clinical relevance since nonspecific thyroid receptor stimulation can produce deleterious side-effects. Here we report that GC-1, a thyromimetic with selective thyroid receptor β action and a potentially limited side-effect profile, promotes in vitro oligodendrogenesis from both rodent and human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. In addition, we used in vivo genetic fate tracing of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells via PDGFαR-CreER;Rosa26-eYFP double-transgenic mice to examine the effect of GC-1 on cellular fate and find that treatment with GC-1 during developmental myelination promotes oligodendrogenesis within the corpus callosum, occipital cortex and optic nerve. GC-1 was also observed to enhance the expression of the myelin proteins MBP, CNP and MAG within the same regions. These results indicate that a β receptor selective thyromimetic can enhance oligodendrocyte differentiation in vitro and during developmental myelination in vivo and warrants further study as a therapeutic agent for demyelinating models.