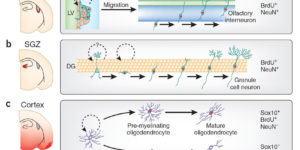
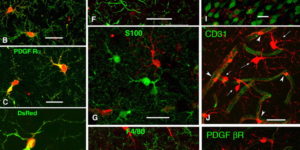
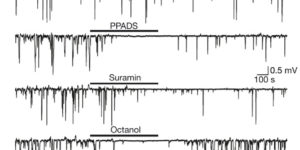
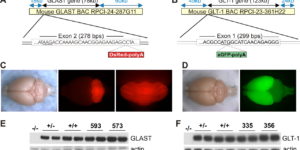
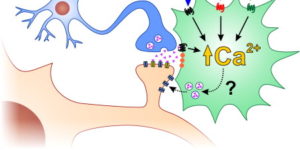
Neuron-glia synapses in the brain
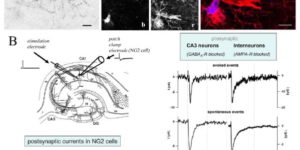
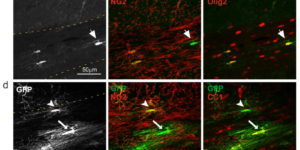
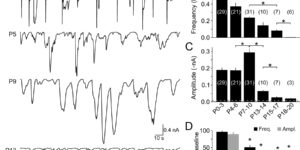
The ability to investigate the electrophysiological properties of individual cells in acute brain tissue led to the discovery that many glial cells have the capacity to respond rapidly to neuronal activity. In particular, a distinct class of neuroglial cells known as NG2 cells, which exhibit many of the properties that have been described for glial subtypes such as complex cells, polydendrocytes, synantocytes and GluR cells, express ionotropic receptors for glutamate and GABA. In both gray and white matter, NG2 cells form direct synaptic junctions with axons, which enable transient activation of these receptors. Electrophysiological analyses have shown that these neuron-glia synapses exhibit all the hallmarks of ‘classical’ neuron-neuron synapses, including rapid activation, quantized responses, facilitation and depression, and presynaptic inhibition. Electron microscopy indicates that axons form morphologically distinct junctions at discrete sites along processes of NG2 cells, suggesting that NG2 cells are an overt target of axonal projections. AMPA receptors expressed by NG2 cells exhibit varying degrees of Ca(2+) permeability, depending on the brain region and stage of development, and in white matter NG2 cells have also been shown to express functional NMDA receptors. Ca(2+) influx through AMPA receptors following repetitive stimulation can trigger long term potentiation of synaptic currents in NG2 cells. The expression of receptors with significant Ca(2+) permeability may increase the susceptibility of NG2 cells to excitotoxic injury. Future studies using transgenic mice in which expression of receptors can be manipulated selectively in NG2 cells have to define the functions of this enigmatic neuron-glia signaling in the normal and diseased CNS.