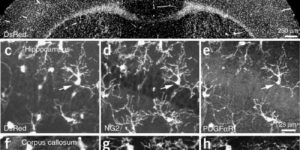
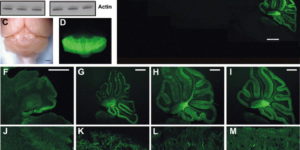
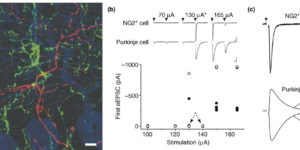
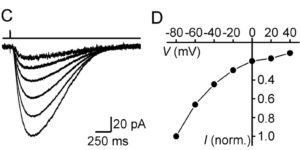
Vesicular release of glutamate from unmyelinated axons in white matter
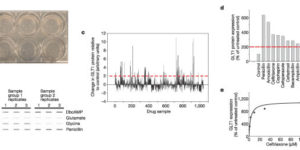
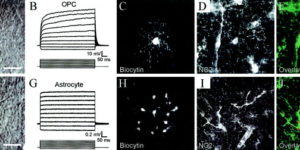
Directed fusion of transmitter-laden vesicles enables rapid intercellular signaling in the central nervous system and occurs at synapses within gray matter. Here we show that action potentials also induce the release of glutamate from axons in the corpus callosum, a white matter region responsible for interhemispheric communication. Callosal axonsreleaseglutamate by vesicular fusion, which induces quantal AMPA receptor-mediated currents in NG2(+) glial progenitors at anatomically distinct axo-glial synaptic junctions. Glutamaterelease from axons was facilitated by repetitive stimulation and could be inhibited through activation of metabotropic autoreceptors. Although NG2(+) cells form associations with nodes of Ranvier in white matter, measurements of conduction velocity indicated that unmyelinated fibers are responsible for glutamatergic signaling with NG2(+) glia. This activity-dependent secretion of glutamate was prevalent in the developing and mature mouse corpus callosum, indicating that axons within white matter both conduct action potentials and engage in rapid neuron-glia communication.