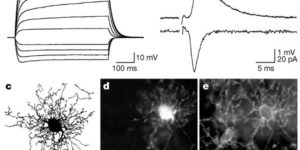
Glutamatergic synapses on oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the hippocampus.
Fast excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system occurs at specialized synaptic junctions between neurons, where a high concentration of glutamate directly activates receptor channels. Low-affinity AMPA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl isoxazole propionic acid) and kainate glutamate receptors are also expressed by some glial cells, including oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs). However, the conditions that result in activation of glutamate receptors on these non-neuronal cells are not known. Here we report that stimulation of excitatory axons in the hippocampus elicits inward currents in OPCs that are mediated by AMPA receptors. The quantal nature of these responses and their rapid kinetics indicate that they are produced by the exocytosis of vesicles filled with glutamate directly opposite these receptors. Some of these AMPA receptors are permeable to calcium ions, providing a link between axonal activity and internal calcium levels in OPCs. Electron microscopic analysis revealed that vesicle-filled axon terminals make synaptic junctions with the processes of OPCs in both the young and adult hippocampus. These results demonstrate the existence of a rapid signalling pathway from pyramidal neurons to OPCs in the mammalian hippocampus that is mediated by excitatory, glutamatergic synapses.